研究現況 / Current Research Projects (2021)
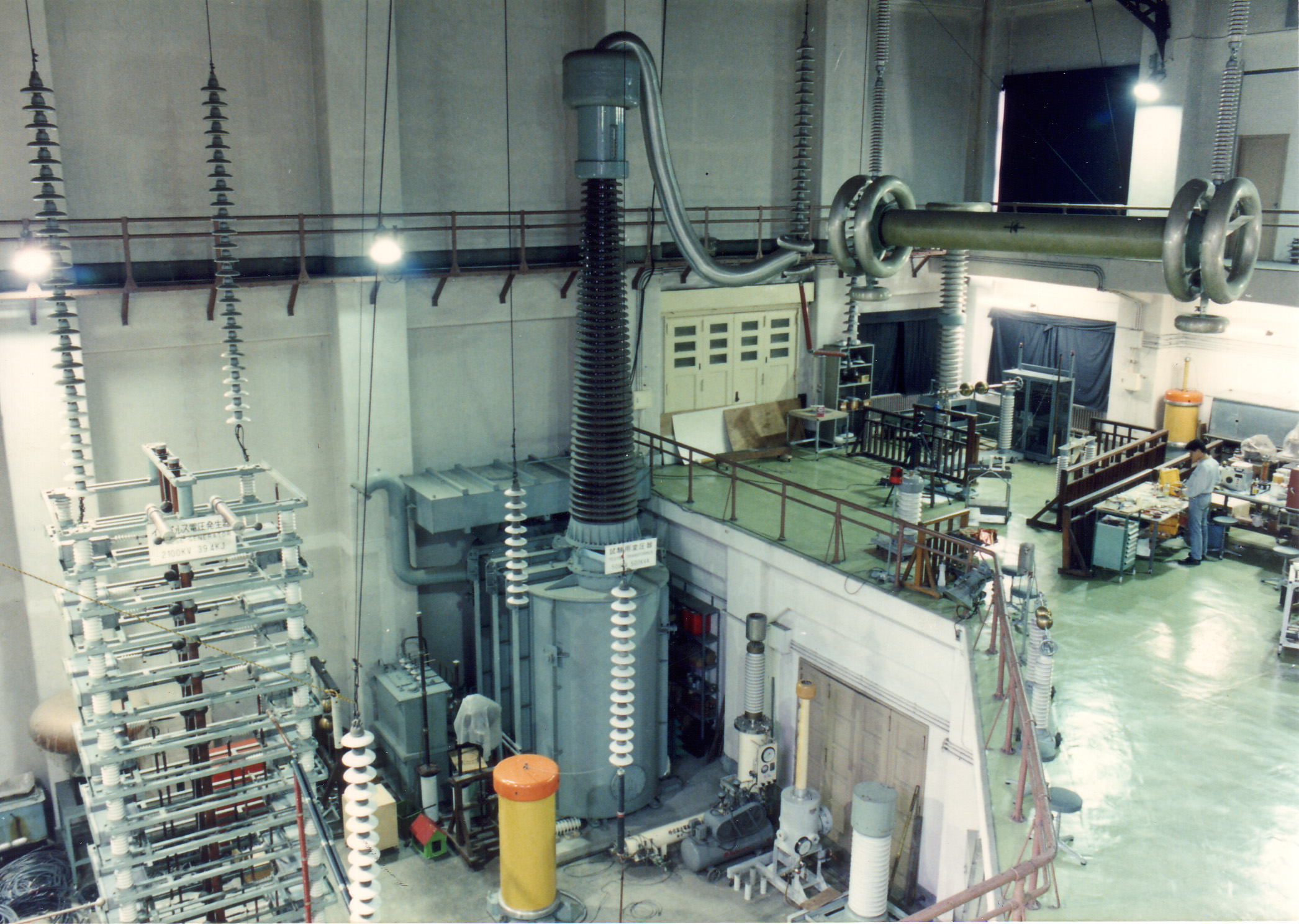
熊田・佐藤&藤井研究室では、計測手法の開発を武器に
- 高電界・放電現象の解明
- 高電圧・大電流機器の絶縁技術
- スマートパワー機器への新展開
等に取り組んでいます。
今年度の詳細な研究現況は以下のようになっています。
The research topic-area are:
- Clarification of high voltage and electrical discharge phenomena
- Insulation technology of high voltage and high current equipment.
- Application to advanced smart power appratus
The details of each topic are listed as follows:
直流電界下における絶縁物の帯電現象
Charge Accumulation on an Insulator under DC Electric Field
Charge Accumulation on an Insulator under DC Electric Field
嶋川肇・岩渕大行・松岡成居・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
H. Shimakawa, H. Iwabuchi, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
H. Shimakawa, H. Iwabuchi, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
ガス絶縁開閉機器(GIS)はその優れた絶縁性能から,主要な電力機器として幅広く運用されている。しかし,GIS内の絶縁スペーサに対して直流電圧が印加された際はスペーサ表面上に帯電が生じ,絶縁破壊電圧が低下するといった問題点が指摘されている。交流GIS (AC-GIS) 内の絶縁スペーサにおいても,スイッチング動作により直流成分の帯電が残留するため,絶縁スペーサ上の帯電現象は問題視されている。そこで本研究では,絶縁スペーサ上の帯電現象について実験と解析の両面から調査を行い,帯電現象の詳細な解明を目指している。主な研究内容は以下の三点である。一つ目として,実験において印加電圧を高圧化することで放電や電子放出が帯電に与える影響を調査している。その中で,三重点付近の電界緩和など実験装置の改良を進めていることも特徴である。二つ目として,絶縁スペーサやSF6ガスの導電率や比誘電率を考慮した上で,帯電現象の数値解析を行っている。この解析では,電流場における連続の式や,ガス中イオンの移流拡散方程式に基づいて数値計算を行う。最後に,GISの絶縁スペーサ上に生じる温度分布が直流帯電現象に与える影響を調査している。実機器のGISでは,通常運転時に高圧母線に生じる電流のジュール熱により電極間の絶縁スペーサには温度勾配が発生し,帯電現象にも大きく影響を与えると考えられる。
Gas insulated switchgears (GIS) are widely used as major substation equipment because of their excellent insulation performance. However, when a DC voltage is applied to an insulating spacer in GIS, charges are accumulated on the surface of the insulator, and the breakdown voltage of it may become low. The charge accumulation phenomenon is also a problem in AC-GIS, because the switching operations may leave the residual DC charges on the AC-GIS spacer. We are now investigating charge accumulation phenomena by conducting both of experiment and numerical simulation and aiming for detailed understanding of the charge accumulation phenomena. First, we are researching the effects of discharge and electron emission on charge accumulation on the spacer surface by increasing the applied voltage on the experiment. Furthermore, this experimental setup is developed in terms of guarding triple junction. Second, the numerical simulation of charge accumulation phenomena is also conducted taking the volume conductivities and relative permittivities of the spacer and SF6 gas into account. It is based on electrical conduction of charge and on advection-diffusion of ions in gas. Third, we are investigating temperature distribution on GIS spacer and its influence on charge accumulation phenomena under DC field. During normal operation where rated current goes through GIS as the load current, a temperature gradient is generated in the insulating spacer between the electrodes, which is considered to greatly affect the charge accumulation phenomena.
真空遮断器における微小粒子起因の遅れ絶縁破壊現象
Late-breakdowns Triggered by Microparticles in Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Late-breakdowns Triggered by Microparticles in Vacuum Circuit Breakers
江尻開・熊田亜紀子・日髙邦彦
H. Ejiri, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
H. Ejiri, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
環境調和性が良く多数回遮断が可能であるなど様々なメリットのある真空遮断器に特有の問題として、大電流遮断後の回復電圧印加から数ms〜数百ms経過後に、遅れ絶縁破壊が生じることが知られている。先行研究から、電極間に存在する微小粒子が遅れ絶縁破壊のトリガになっているという説が有力とされているが、実際に粒子の運動の様子を詳しく観測した例はなく、遅れ絶縁破壊発生のメカニズムは未解明であった。本研究では主に2つのアプローチから、微小粒子に起因した遅れ絶縁破壊の解明を試みた。まず、左図に示す微小粒子注入実験では、金属-真空-金属からなる真空ギャップに意図的に微小粒子を投入し、直流の高電圧を印加した際の微小粒子の挙動と絶縁破壊の関係を調査した。その結果、微小粒子に起因した絶縁破壊は、絶縁破壊前の微小粒子の挙動、絶縁破壊時の発光の場所、絶縁破壊後の微小粒子の挙動から6つのパターンに分類できることを明らかにした。次に、琉球大学、埼玉大学、横浜国立大学と共同で行った右図に示す電流遮断試験では、ピーク値数kAの大電流遮断後の回復電圧印加時に生じる微小粒子起因の絶縁破壊の例を世界で初めて鮮明に捉えた。この映像は、2018年にドイツで行われた国際学会(ISDEIV2018)において「Best Video Award 2018」を受賞した。
In the vacuum circuit breakers, it is well known that there is some possibility of the occurrence of the breakdowns several to hundreds of milliseconds after the circuit current is interrupted. These late-breakdowns are thought to be triggered by the microparticles existing in the vacuum gap. However, the triggering mechanisms of these late-breakdowns are still unknown despite the efforts of the many researchers in the long history of the vacuum interruption technology. In this study, the relation between microparticles and the late-breakdowns are clarified using mainly two approaches. Firstly, left figure shows the concept and the main result of the microparticle artificially injection test. Microparticles were artificially injected to the vacuum gap composed of electrode-vacuum-electrode, then the DC high voltage was suddenly applied to the gap. The motion of the microparticles and the breakdowns were observed by a high-speed video camera and a voltage divider. We found that the breakdowns triggered by microparticles can be grouped into six patterns according to the motion of the microparticle before the breakdown, the place of the light emission, the motion of the microparticle after the breakdown. Secondly, right video shows the summary of the circuit current interruption test collaborated with University of the Ryukyus, Saitama University, and Yokohama National University. During the recovery voltage application after the circuit current is interrupted in the vacuum gap, we observed clear evidence of the late-breakdowns triggered by the microparticle emitted from the electrode. This video won “Best Video Award 2018” at the ISDEIV 2018 held at INP, Greifswald, Germany.
エポキシ樹脂中の電気トリー作成と観察
X-ray visualization of the electrical tree in epoxy resin
X-ray visualization of the electrical tree in epoxy resin
横井稜樹・松岡成居・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
T. Yokoi, M. Matsuoka, A.Kumada, and K. Hidaka
T. Yokoi, M. Matsuoka, A.Kumada, and K. Hidaka
電気トリーとは、固体材料中にできる微小な空孔であり、有機絶縁材料の内部または導体との界面にボイドやクラックなどの空隙が存在すると部分放電が生じ、トリーが発生、それが絶縁物中を進展していき最終的に全路破壊へ至ることが知られている。しかしながら、実機で使用されるエポキシ樹脂等は充填剤により不透明で、トリーの様子を観察するのは難しい。近年X線位相イメージングを用いたトリー観測手法が注目されているが、充填剤がX線を吸収し、電気トリー像の取得を妨げている。そこで、本研究では電圧印加前・印加後の差分画像を取得することで、充填剤入りエポキシ樹脂中のトリーの観察を行った。電圧を印加しながら、非破壊的にトリー進展様相の観察に成功した。また、X線CTを用いて3次元位相イメージングすることで,エポキシ内部のトリー像を取得した。トリーの半径や体積が取得できることがわかった。
Electrical trees are very small holes in an organic polymer. Electrical trees initiate and extend when partial discharges occur in a void or crack. Finally breakdown occurs. Epoxy resin in electrical apparatus is opacity because it contains filler. Therefore, it is difficult to observe electrical trees in epoxy resin. Recently, X-ray phase imaging has attracted a lot of attention as a method to observe tree shape and propagation. However, observation of trees in filled epoxy is challenging because silica particles absorb X-rays and disturb the acquisition of a clear image of treeing. In this study, image subtraction was applied to overcome this issue and time evolution of treeing was observed. Electrical trees in epoxy resins with 1.5 μm and 5 μm silica fillers were successfully observed. 3D imaging by X-ray CT of electrical trees is obtained. The detail of tree characteristics such as volume and tree diameter can be obtained by this method.
パワーモジュール絶縁ゲル中の電気トリー
Electrical Trees in Gel for Power Modules
Electrical Trees in Gel for Power Modules
中村信・佐藤正寛・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
S. Nakamura, M. Sato, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
S. Nakamura, M. Sato, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
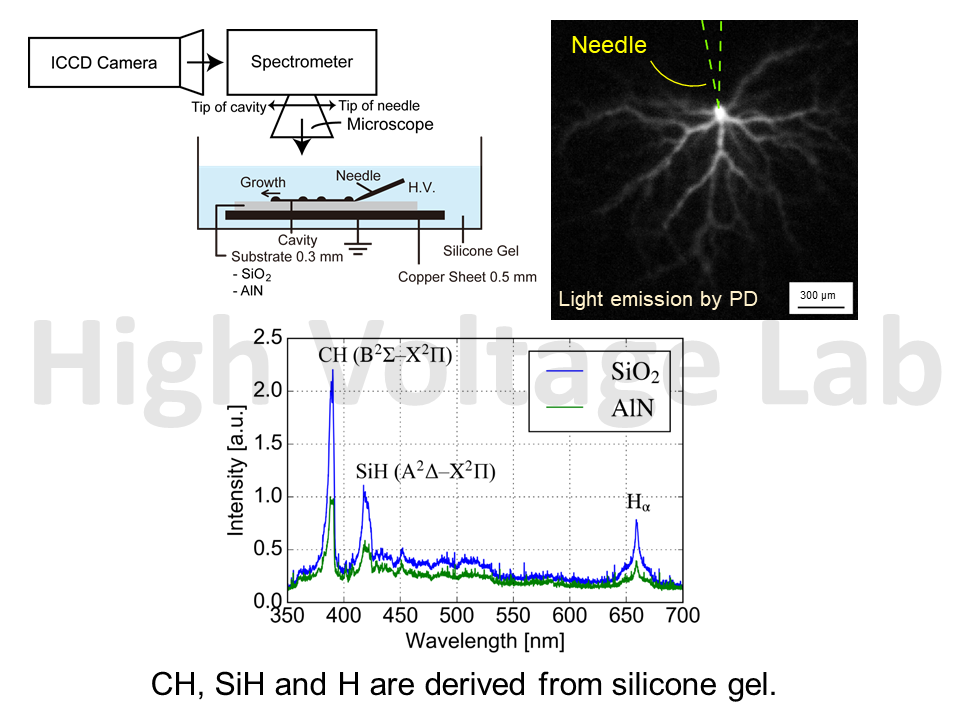
パワーモジュールの動作電圧の高圧化・動作周波数の高速化から電気絶縁の信頼性確保が懸念される。パワーモジュール内の絶縁上の最弱点は、基板と素子と絶縁封止材(シリコーンゲル)との三重点であり、そこからキャビティー(電気トリー)と呼ばれる絶縁劣化が生じ、やがて破壊に至ると考えられる。従来、正弦波交流電圧下でゲル中の絶縁劣化の研究はなされてきた。しかしながら、パワーモジュールは矩形波パルス電圧を組み合わせたPWM波形で運転される。そこで、繰り返しインパルス電圧下におけるゲル中の劣化現象について調査したところ、周波数が高くなるほど、また立ち上がり時間が短くなるほど絶縁劣化のリスクが急増する可能性を明らかにした。また、劣化メカニズムを詳しく調査するため、キャビティー内の部分放電発光を分光することで、化学的組成を調査した。キャビティーは絶縁基板によらずシリコーンゲルが分解したものから形成される可能性が明らかとなった。
Silicone gel is widely used to encapsulate power modules. The weakness of the electrical insulation is surface discharges initiating at the gel-substrate-electrode triple junction and the subsequent formation of cavities, so called electrical trees. The propagation characteristics of cavities under high frequency and fast rise time voltages, which are typical waveforms formed in power modules, have not been fully understood. Thus, in this research, the influence of frequency, rise time on electrical treeing under repetitive voltage impulses are investigated. The results show that the cavity length increases with the frequency and is especially long when the rise time is short under high frequency. Chemical production process of cavity propagation is still unknown. A spectroscopic study is, therefore, conducted on light emission by PD in cavity. Spectra of CH, SiH, and H were observed. It suggests that the cavity is filled with products from gel.
Quantitative evaluation of charge transfer in insulating material, based on first principles calculation
M. Sato, A. Kumada, K. Hidaka, T. Hirano and F. Sato
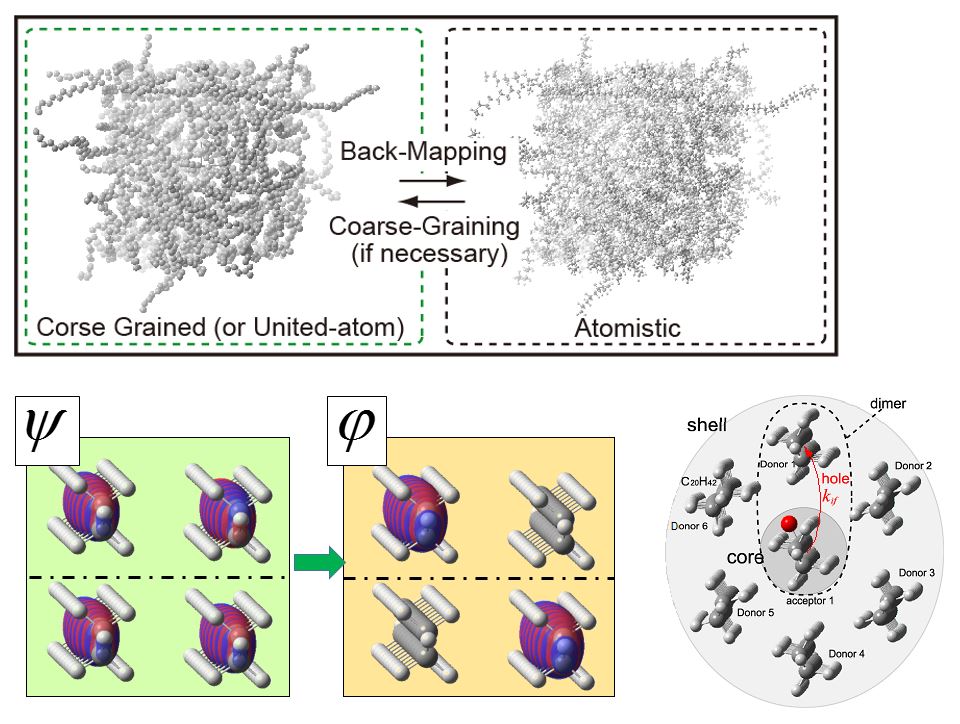
Polymeric insulators are extensively used in high voltage applications. In order to improve the reliability, durability, operating voltage, compactness, cost-efficiency and functionality of electric power equipment and transmission cables, it is necessary to understand the aging process of polymeric insulators. Although it is widely accepted that degradation of polymers are correlated with space charge which is formed in the material [1,2], there remains a lack of understanding of charge transfer (CT) phenomena, despite extensive experimental efforts. One of the most fundamental parameters required to understand CT is charge carrier mobility of the material. Unfortunately, we are still far from computing charge carrier mobility in polymeric insulators without any ad hoc assumptions or parameters; moreover we can hardly discuss qualitative characteristics of mobilities in most electrically insulating materials. This is partly due to the fact that although CT in solids is intrinsically quantum mechanical, we were unfamiliar with such treatment. Considering the above, in this research, hole mobility in polyethylene (PE) is calculated by means of standard density functional theory. It turns out that hole transfer in PE occurs in a “hopping regime”. In addition it was shown that hole mobility in PE is smaller by more than five orders of magnitude than that in naphthalene; both due to small electronic coupling between molecules and large activation energy. In addition, it is implied that the existence of carbonyl defect is likely to increase hole mobility which is consistent with experimental results at least for low density PE.
レーザ波面計測によるアーク放電中の乱流測定
Turbulence Measurement in Arc Discharge by Wave-front Sensor
Turbulence Measurement in Arc Discharge by Wave-front Sensor
菊池諒・稲田優貴・松岡成居・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
R. Kikuchi, Y. Inada, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
R. Kikuchi, Y. Inada, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
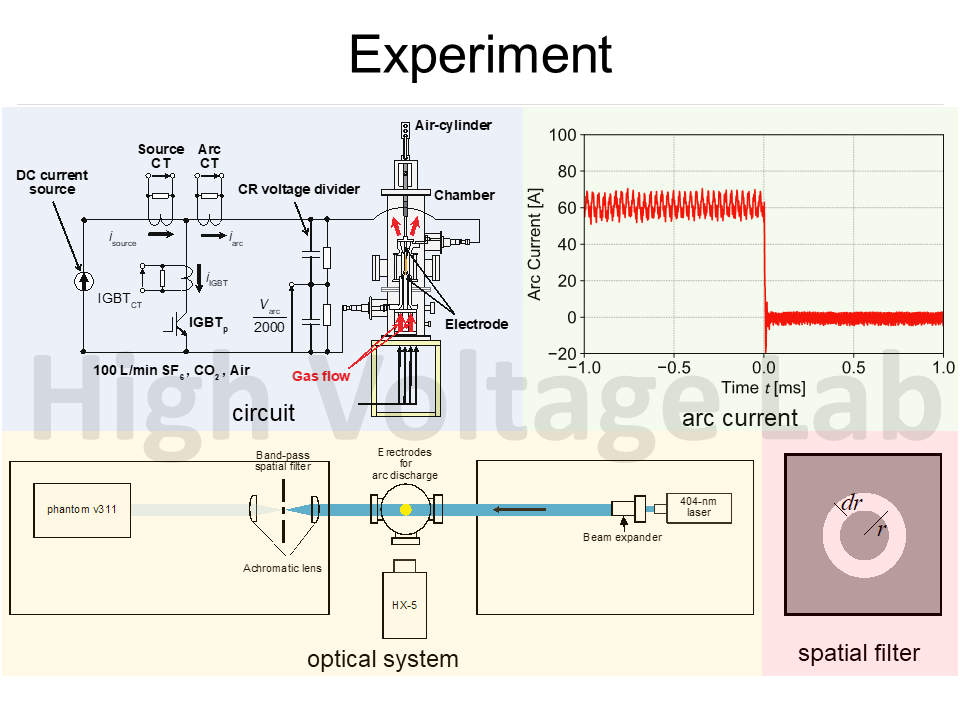
現在、高圧系統で利用されているガス遮断器では温暖化係数の高いSF6ガスが主に使用されている。代替ガスの開発を行うためにはSF6ガス中アークの消弧機構を解明する必要がある。本年度はバンドパス空間フィルタを用いたレーザ波面測定装置により、消弧アーク内における乱流構造の可視化を行った。その結果、乱流構造はSF6が最も細かく、次いでCO2、Airであった。SF6の高い消弧性能は、微細な乱流によるエネルギー損失の増大に起因することが示唆された。
In high voltage power network, SF6 gas with high global warming potential is mainly used as an arc-quenching media in gas circuit breakers. In order to develop the SF6-alternative gas, it is required to elucidate the quenching mechanism of SF6-gas arcs. The laser wave-front sensors with band-pass spatial filters were used for measuring turbulence structures over long-gap decaying arcs in a free-recovery condition confined by a gas-blast nozzle simulating an actual arc-quenching chamber in gas circuit breakers. As a result, the turbulent structure was finest for SF6, which was followed by CO2 and air. This result suggests that the superior arc-quenching-capability of SF6 is achieved by the fine-turbulent-induced energy loss from the arcs.
レーザを用いた遠隔・非接触計測技術
Remote and non-contact measurement using laser
Remote and non-contact measurement using laser
藤井隆・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
T. Fujii, A.Kumada, and K. Hidaka
T. Fujii, A.Kumada, and K. Hidaka
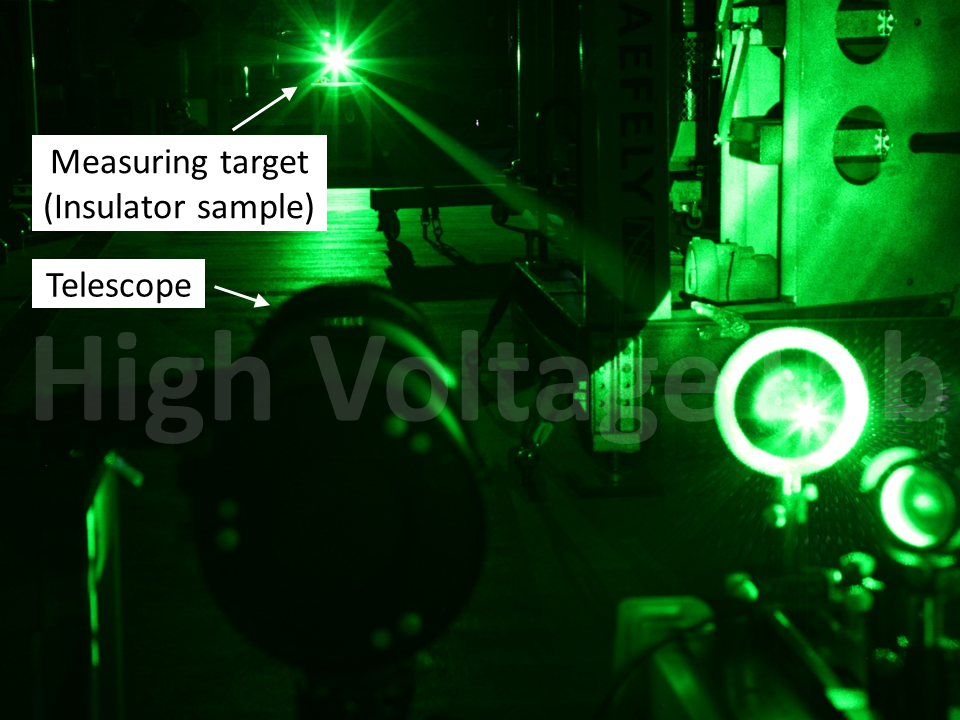
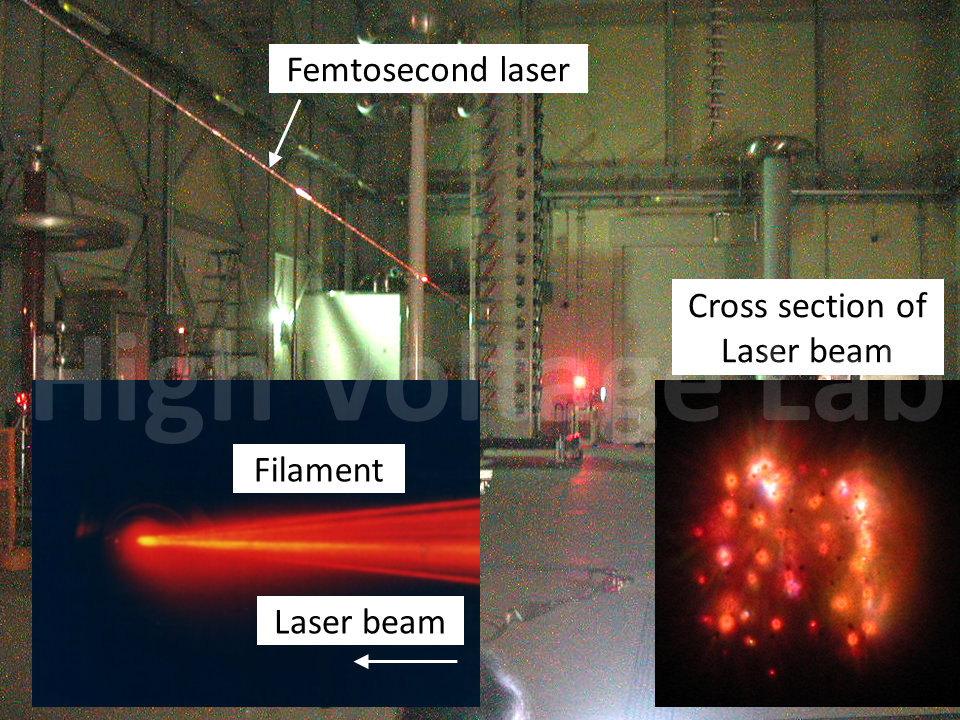
レーザー光を測定対象物に集光することによりプラズマ化し、このプラズマからの発光を分光・解析することで,対象物に含まれる元素を測定することができる。このような測定方法はレーザー誘起ブレイクダウン分光法(LIBS: Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy)と呼ばれている。LIBSの主な特長は、その場で計測ができること、対象物から離れた位置からの測定(リモートセンシング)が可能なことである。当研究室では、このLIBSを用いた様々な計測・診断技術に関する研究を行っている。また、パルス幅がフェムト秒、ピークパワーがテラワットの超短パルスレーザ光を大気中で伝搬させると、カー効果による自己収束が生じる。これにより、大気がプラズマ化し、発生したプラズマによりレーザ光の発散が生じる。このカー効果による自己収束とプラズマによる発散が繰り返されることにより生成する特殊なレーザー光はフィラメントと呼ばれており、このとき生じる細長いプラズマはフィラメントプラズマと呼ばれる。フィラメントプラズマは、それ自体が研究対象であるだけでなく、放電誘導や遠隔計測、THz発生等の応用研究にも用いられる特異なプラズマである。当研究室では、この超短パルスレーザー生成フィラメントの基礎物理の解明と、その計測・診断技術の開発や放電研究への応用に関する研究を行っている。
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is an attractive tool for the in-situ and remote measurement of elements attached on or contained in a target. In this method, the laser beam is focused on the target to produce plasma, of which emission is analyzed spectroscopically. We are developing methods of measurement and diagnostic for the application to such as electric power equipment using LIBS. On the other hand, when femtosecond-terawatt laser pulses are propagated in the atmosphere, self-focusing is occurred by Kerr effects to produce plasma which defocus the laser pulses. The unique phenomenon, called laser filamentation, is occurred by the equilibrium between self-focusing by Kerr effects and plasma defocusing, and long and thin plasma, called filament plasma, is produced. The filamentation itself is a unique target of research, and also can be applied for discharge triggering, remote measurements, and terahertz radiation. We study on the basic physics of the filamentation and its application to the measurement, diagnostics and a tool to study discharge phenomena.
CF3I混合ガスの特性測定とフレキシブルGILへの応用
Discharge characteristics of CF3I gas mixture and its applicability to Flexible Gas Insulated transmission Lines
Discharge characteristics of CF3I gas mixture and its applicability to Flexible Gas Insulated transmission Lines
小林拓人・松岡成居・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
T. Kobayashi, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
T. Kobayashi, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka

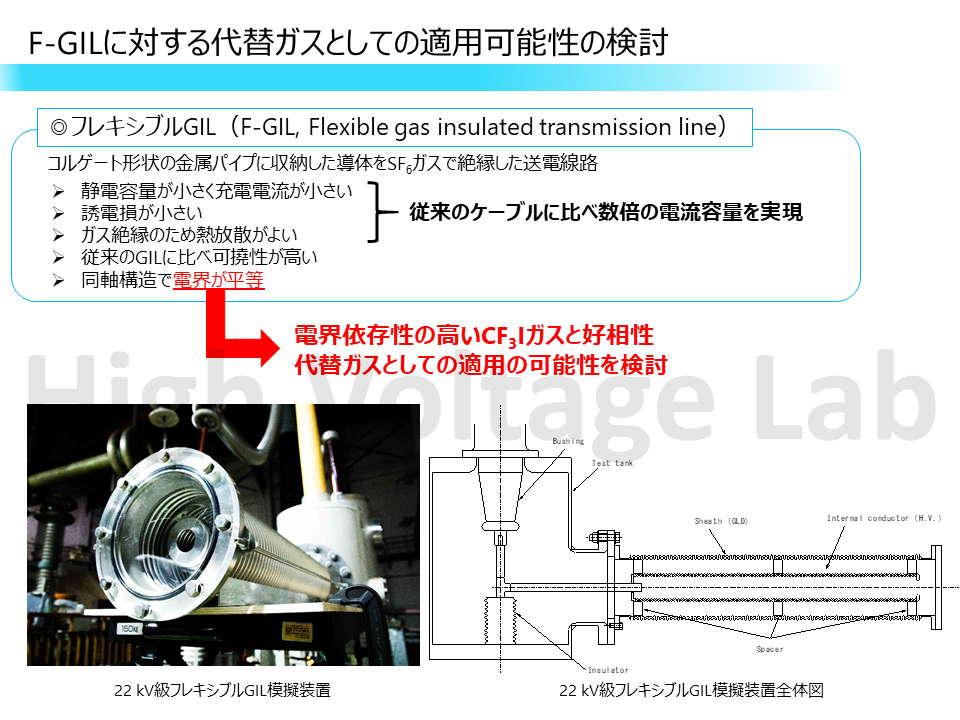
SF6ガスは高性能な絶縁ガスとして電力機器に広く用いられてきたが、CO2の23,500倍というその高い温室効果から近年では使用が制限され、代替ガスの模索が急務となっている。当研究室では代替ガスの中でも特にCF3Iガスに着目して研究を行っている。過去の研究においてCF3IをGIL(管路気中送電線)に使用することが有望であると結論付け絶縁性能、伝熱性能などの観点からCF3I混合ガスを用いたGILの概念設計を行い適用の可能性を検討した。現在はGIL、及びGILにコルゲート状の加工を施し可撓性を改善させたフレキシブルGILについて実機を模擬したモデルを用いて試験を行いCF3I混合ガスの適用可能性を検討中である。
SF6 gas is commonly used for high-voltage apparatus due to its superior properties as an insulation medium. However, SF6 has a considerably negative impact on the environment, so its use and emission are requested to be regulated. As an alternative insulation medium, CF3I came under the spotlight in our study. It is concluded that it is promising to use CF3I for GIL (Gas Insulated transmission Line) in our past research, and conceptual design of GIL using CF3I mixed gas is performed from the viewpoint of insulation performance, heat transfer performance etc. At present, the applicability of CF3I mixed gas for GIL and Flexible-GIL is tested using a model simulating an actual machine.
ポッケルス効果を用いた電圧回転機電界緩和システムの電位分布計測
Potential Distribution Measurement on Stress Grading System of High-Voltage Rotating Machines by Using Pockels Effect
Potential Distribution Measurement on Stress Grading System of High-Voltage Rotating Machines by Using Pockels Effect
小野田貴亮・松岡成居・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
T. Onoda, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
T. Onoda, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
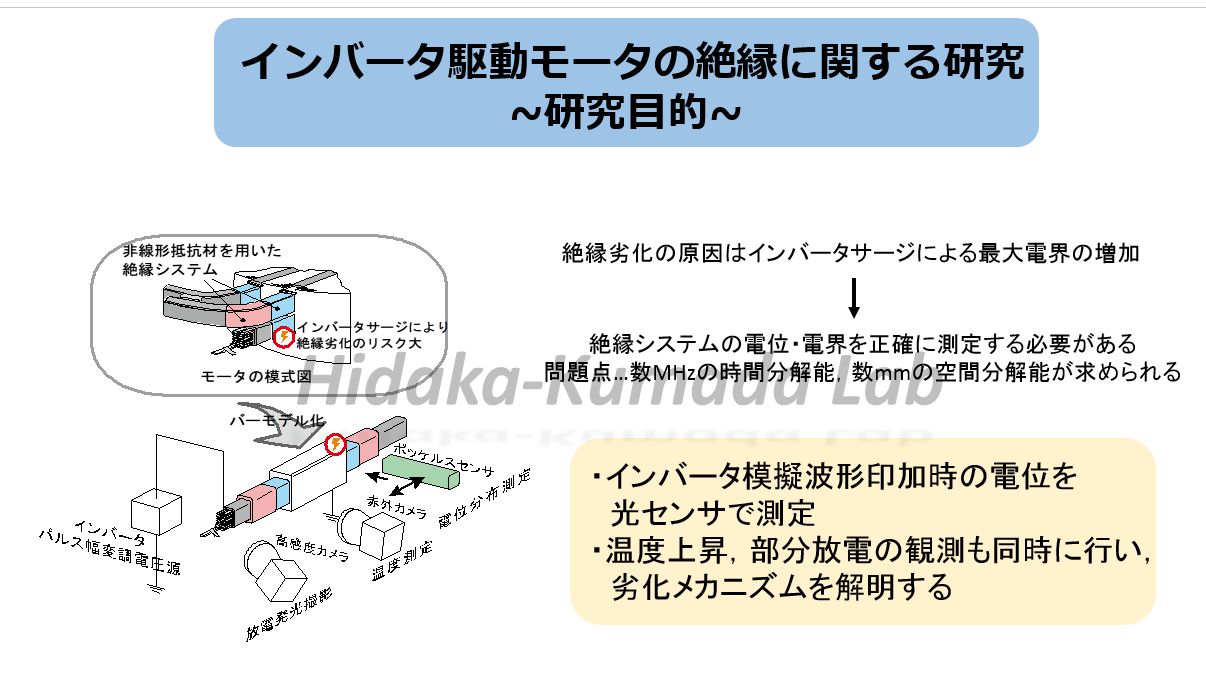
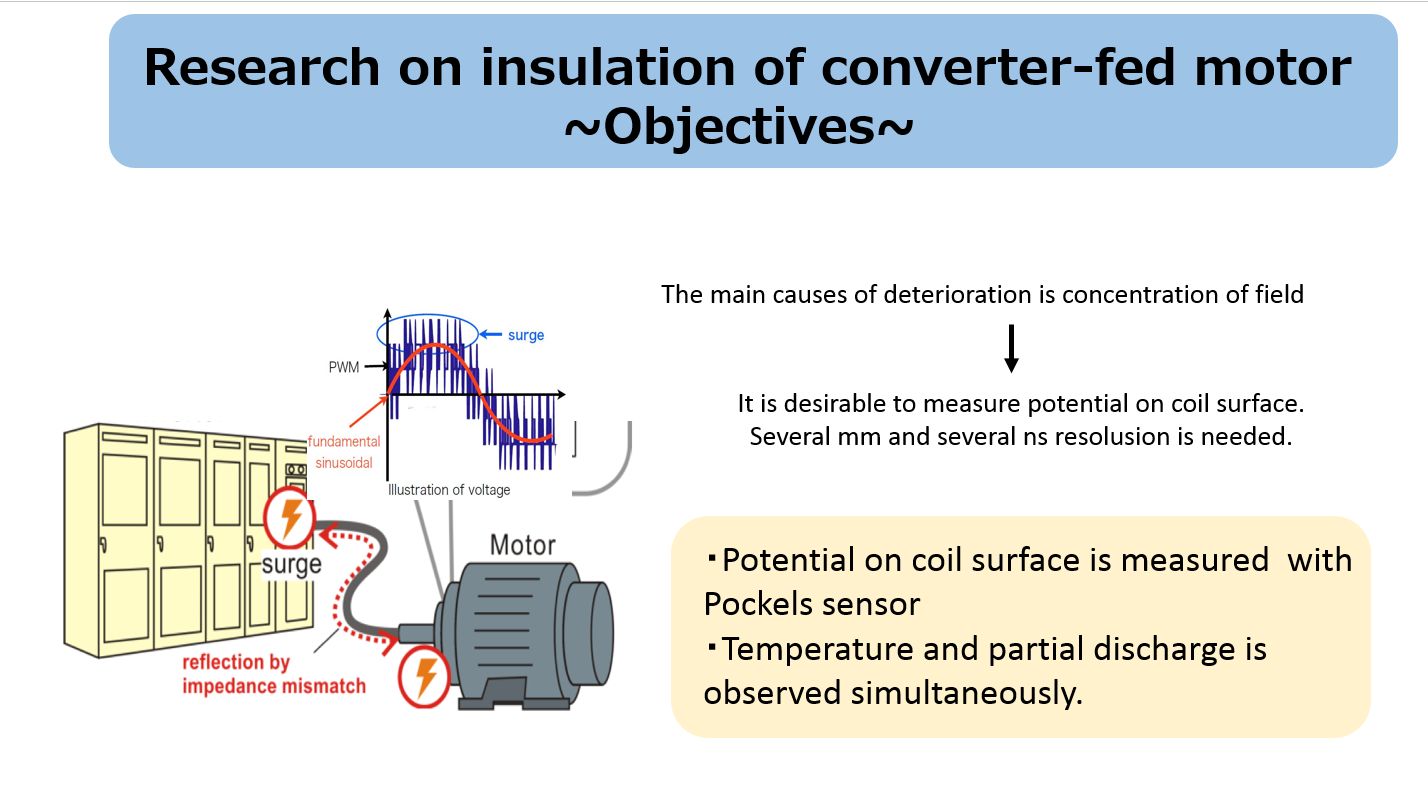
近年,省エネルギー化や制御の容易さの観点からインバータ駆動モータの導入が増加している。それに伴いインバータサージがモータの絶縁に与える影響が懸念されている。高圧モータにおいては鉄心付近の電界緩和システムの劣化が指摘されており,インバータ駆動に対応した絶縁設計をするために,電界緩和システムの表面電位分布を実測して評価することが望まれる。本研究では、高電圧を印加時の電界緩和システム表面の電位分布測定を行うため,ポッケルス効果を用いた測定システムの開発を行った。本測定システムを用いて,250nsで立ち上がる繰り返しインパルス印加時の電位分布を測定した。同時に温度分布の測定,部分放電の観測も行った。その結果,繰り返しインパルス印加時には立ち上がり時には低抵抗層部に,立ち下がり時に半導電層部に強い電界ストレスがかかっていることが明らかになった。
The importance of inverter fed drives to control high voltage motors has been increasing for energy saving. However, these drives using pulse width modulation are known to have adverse effects on the insulation system for motors especially in which stress grading materials are used in the end-winding design. The experimental information on the potential distribution is essential for advanced designing of end-winding insulation system. In this study, a surface potential measuring system is developed utilizing Pockels sensor in longitudinal mode and applied it to the potential distribution measurement on the stress grading system of a model bar-coil under repetitive impulses, PWM voltages, DC biased voltage. In addition, measurement of temperature distribution and observation of light emission have been conducted. As a result, it turns out that under the application of repetitive impulses electrical field is concentrated on the corona armor tape during the wave-front, and on the semi-conductive tape during the wave-tale. In addition, computed results which are consistent with measured result has been obtained by using FEM. We can propose a more reliable insulation system with this analysis.
Kerr効果を利用した電界測定システムの広帯域化
Expansion of Response Bandwidth of Electro-optic Sensors by 200MHz-Modulation Technique
-Measurement of Poisson’s field-
Expansion of Response Bandwidth of Electro-optic Sensors by 200MHz-Modulation Technique
-Measurement of Poisson’s field-
佐藤正寛・松岡成居・熊田亜紀子・日高邦彦
M. Sato, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka
M. Sato, S. Matsuoka, A. Kumada, and K. Hidaka

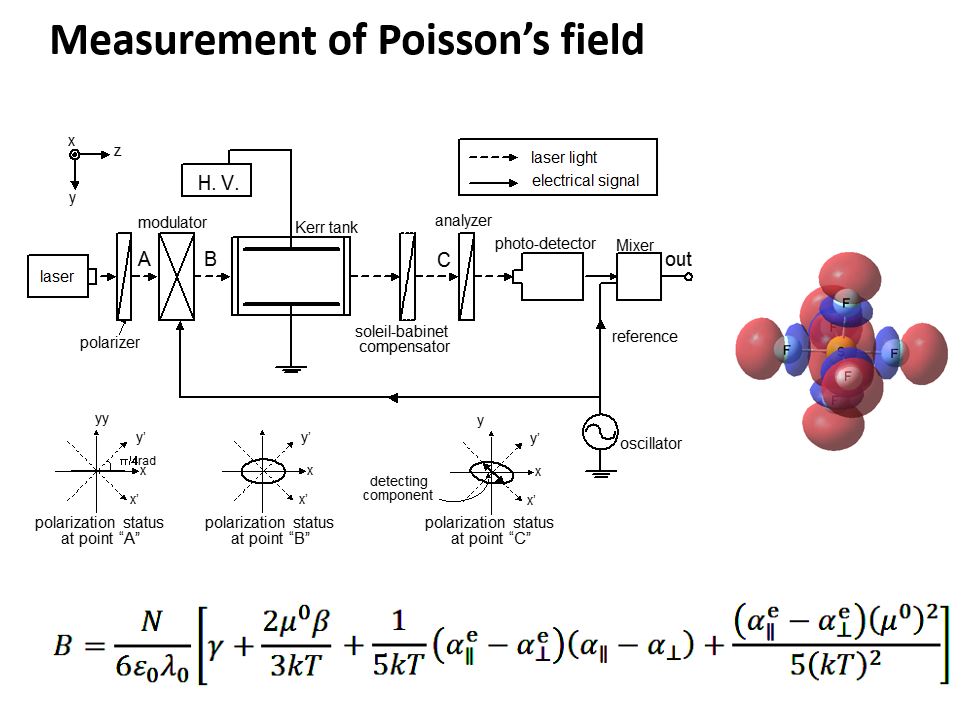
二次の電気光学効果である気体Kerr効果を用いた電界測定法は、媒質自体が持つKerr効果を利用するため、汎用性が高い測定法であると考えられるが、気体のKerr定数はきわめて微小な値であり、気体中の電界測定にKerr効果を利用するのは困難であるとされてきた。ところが近年、光学的変調手法を導入した高S/N比測定装置を用いることにより、気体Kerr効果を利用した電界測定が実現されつつある。この測定法は、光が有する電磁無誘導性、電気絶縁性、広帯域性などの特長を最大限に活用することができる。任意の気体を挿入できるKerr効果測定装置を用いて、従来の帯域では測定不可能とされていた雷インパルス電界の測定を実現した。
Electric field measurement method using Kerr effect in gas is considered to be a highly versatile measurement method, because all substances have Kerr effect. However, since the Kerr constant in gas is very small value, it has been difficult to utilize Kerr effect when measuring electric field in gas. In recent years, by using a high S/N ratio measuring apparatus which introduces an optical modulation scheme, the electric field measurement using Kerr effect in gas is being achieved. This measurement method can make the most of features of light: non-magnetic induction, electric non-conductance, and broadband performance. In this study 200MHz modulation technique is developed for expanding the response bandwidth of electro-optic sensor. With this technique, lightning impulse electric field, which has been considered hard to measure in a conventional method, is successfully measured by using Kerr effect in gas. In order to quantitatively examine the measurement capability of Poisson’s field using electro-optic Kerr-effect (EOKE), Kerr constants of neutral molecules and ions were examined. Kerr constants are determined by dipole moment, polarizability, and hyper polarizability of molecules. Since these values are fundamentally quantum mechanical, computations was done by means of first principle quantum chemistry methods. The computed Kerr constants for neutral molecules (N2, CO2, SF6 and CF3I) were within 50% error of the experimental values, comparable to the scattering between experimental values itself. The results showed that SF6 has smaller Kerr constants compared to those of N2 and CO2 due to its high molecular symmetry. In contrast, CF3I has higher Kerr constant due to its permanent dipole. The computed Kerr constants for anions were larger by two orders of magnitude than those of neutral molecules. The difference is probably due to the shielding effect; electrons of anions are less attracted to the nucleus and likely to polarize under external electric field. For cations, the opposite holds true. However Kerr constants contain the anisotropic polarizability term, which is strongly influenced by the anisotropy of electron density distribution, and thus can be larger for cations. As a result, the calculated Kerr constants of cations were comparable to or smaller than those of neutral molecules. The ratio of Kerr constants of ions to those of neutral molecules did not exceed 103. Thus it was shown that EOKE is valid for measuring electric field in weakly ionized gas whose ionization degree is smaller than 10-3. Poisson’s field in air at atmospheric pressure was measured by means of EOKE measurement. It was shown that we have to compensate the change in number density of neutral molecules when measuring unstable discharges.